Cancer Care
Compassionate & Integrated Cancer Care
Cancer diagnosis is a sensitive subject. Personalized treatment plans paired along with our highly trained and compassionate care team is one of the most vital elements in patients’ journey through cancer. Our medical care combines clinical innovation, patient-centered care, HOPE, and to deliver the best quality and individualized cancer treatment.
Personalized and Innovative Treatment Plans
Dedicated and Experienced Cancer Care Team
Supported with Multidisciplinary Services
State-of-the-art Technology
Cancer Care Services and Facilities
Columbia Asia Hospitals offer cancer care services, focusing on diagnosing and treating cancers through various modalities of treatment for each type of cancer diagnosis.
- Cancer Screening & Diagnostics Cancer Treatments
- Surgery
- Chemotherapy
- Radiotherapy
- Cell-Based Immunotherapy
- Interventional RadiologyPost-Treatment Care
- Cancer Rehabilitation Program
- Dietary Consultation
- Palliative Care
- Multi-disciplinary Speciality Care
- Pain Management
- Home Care
- Patient Group Support
- Cancer Screening & Diagnostics Cancer Treatments
- Surgery
- Chemotherapy
- Radiotherapy
- Cell-Based Immunotherapy
- Interventional RadiologyPost-Treatment Care
- Cancer Rehabilitation Program
- Dietary Consultation
- Palliative Care
- Multi-disciplinary Speciality Care
- Pain Management
- Home Care
- Patient Group Support
Treatments and Procedures
Before receiving treatment, do not hesitate to speak to our oncologists, radiation therapists or oncology nurses if you have any questions or concerns about possible side effects. Our medical team will help you gain a better understanding of your treatment and how to manage these side effects.
Cancer surgery is the oldest and one of the main cancer treatments. It is performed to remove tumor and its surrounding tissues at an early stage. Cancer surgery may be offered to advanced cancer stage patients after chemotherapy or radiotherapy which aims to shrink the tumor size. Types of cancer surgeries include curative surgery, preventive surgery, diagnostic surgery, staging surgery, debulking surgery, palliative surgery, supportive surgery and restorative surgery.
Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses anti-cancer drugs as part of a standardized chemotherapy regime to target and kill cancer cells. It is intended to halt the progression of cancer, prolong life or reduce symptoms for an improved quality of life.
In the treatment of blood cancers such as leukaemia or lymphoma, high-dose chemotherapy is usually given. Chemotherapy is used to kill all cancer cells prior to the transplant of new, healthy blood cells, usually done one or two days later.
Chemotherapy makes cancer cells more sensitive to subsequent radiation therapy. When given in combination, the treatment is called chemoradiation. It is commonly used to treat cancers of the brain, bowel, cervix and esophagus.
Some cancers, such as breast or prostate cancer, may progress in response to patient’s own hormone signaling. Hormone therapy, usually administered as tablets or injections, aims to slow down or stop the growth of cancer cells by blocking these signals. This form of treatment may be given following chemotherapy.
Targeted therapies are drugs designed to recognize distinct features or molecular targets, on specific cancer cells. The drug identifies and attacks the cancer cells to stop its growth and spread. Often combined with chemotherapy, these drugs may be given intravenously, as injections or in the form of oral tablets.
Immunotherapy helps your body’s own immune system fight cancer cells. There are several types of immunotherapy, all with different mechanisms of action. As an example, checkpoint inhibitors work to remove barriers that prevent the immune system from detecting and destroying cancer cells. Immunotherapy is usually given intravenously, and may be combined with chemotherapy.
6 Dimension Robotic couch top (HexaPOD)
Counter the pitch, roll and yaw.
Uninterrupted arc treatment
Fast treatment delivery to reduce risks of motion and discomfort.
Provides more comfort to patients during treatment.
Specifically targets tumor with minimal radiation to surrounding tissues.
3D and 4D imaging with capabilities to visualize very small and moving tumors.
Consists of two energies:
- Photon: Better penetration towards deep-seated tumors
- Electron: Effective for superficial tumors
Your radiation oncologist and medical physicist will formulate a treatment plan to accurately target cancer cells and minimize radiation to the surrounding healthy tissues, thus reducing side effects.
-
Step 1 Consultation

- Your oncologist will ask questions about your medical history and your needs.
-
Step 2 Computerized Tomography (CT) Simulation
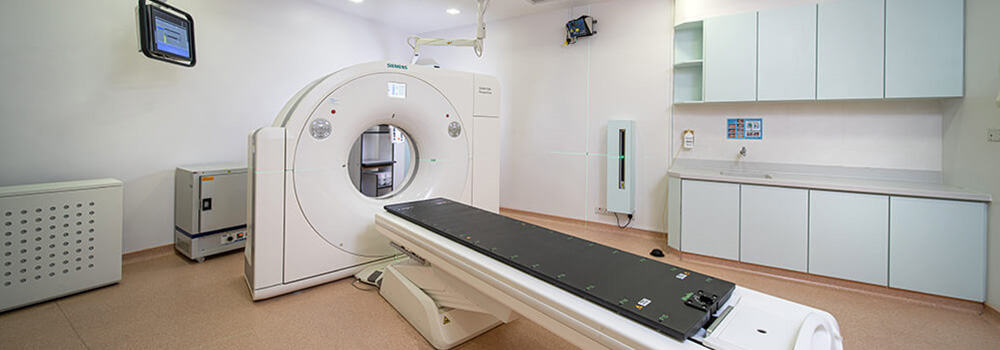
- This is a mapping of the specific area of treatment. The simulation will be produced using a CT scanner for greater precision and accuracy.
-
Step 3 Treatment Plan
- Your treatment plan can be customized in order to achieve the best outcome possible.
-
Step 4 Treatment
- Radiotherapy is given using a linear accelerator machine.
-
Step 5 Follow-Up
- It is vital to have your progress monitored and to check for side effects.
We offer the following radiotherapy treatment techniques:
- Three-Dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy (3D-CRT)
- 3D-CRT shapes the radiation beam to match shape of the tumor with the acquired 3D-image during computerized tomography (CT) simulation.
- Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy (IMRT)
- IMRT is an advanced type of radiation therapy used to treat cancer and non-cancerous tumors.
- Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT)
- VMAT is an advanced technique that delivers the radiation dose continuously as the treatment machine rotates. It focuses the radiation on the tumor while protecting healthy tissues.
Generally, there is a concern that high levels of radiotherapy may result in a new tumor. However, the risk of this happening is exceedingly low. The benefits of radiotherapy far outweighs the risks of severe adverse effects.
- VMAT is an advanced technique that delivers the radiation dose continuously as the treatment machine rotates. It focuses the radiation on the tumor while protecting healthy tissues.
- Palliative Radiotherapy
- Palliative radiotherapy aims to alleviate the symptoms.
- Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT)
- SBRT is a type of external beam radiation that allows highly precise delivery of high doses of radiation in a shorter course of treatment.
- Stereotactic Radiotherapy / Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRT/SRS)
- SRT is a type of external radiation therapy which uses special equipment to precisely position the patient in order to deliver radiation to a well-defined brain tumor.
SRS and SRT are very similar, but SRS delivers a large dose of radiation on a single day and SRT has a fractionated treatment schedule. This means that in an SRT treatment the patient will have treatments spanning multiple days.
- SRT is a type of external radiation therapy which uses special equipment to precisely position the patient in order to deliver radiation to a well-defined brain tumor.
- Image Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT) - 4D CBCT (Symmetry), CBCT (Cone Beam CT) & kV (xvi)
- IGRT is the use of imaging during radiation therapy to improve the precision and accuracy of treatment delivery.
- Active Breathing Coordinator (ABC)
- ABC devices are used during radiation therapy to employ moderate deep inspiration breath-hold (DIBH) techniques to reduce dose to other organs at risk.
Cell-based immunotherapy is using strategies to help immune cells recognize tumor antigens and then destroy the cancer cells. These promising immunotherapy strategies for cancer treatment have been extensively studied by academic research institutions and the pharmaceutical industry.
Interventional radiology involves the use of medical imaging to see inside the body coupled with minimally invasive techniques to diagnose and treat cancer, as well as provide relief from symptoms.
The Triage System
The A&E department follows a triage system to prioritize patients based on the severity of their condition. This ensures that critical cases receive immediate attention and that resources are allocated appropriately. While waiting times may vary depending on the urgency of each case, the staff at Columbia Asia Hospital strives to minimize waiting times and provide timely care to all patients. Below is an example of a triage system:
Triage 1 Critical (Red Zone) IMMEDIATE
This denotes patients who are unstable or when there is a potential loss of life or limb. For example:- Cardiac arrest
- Severe respiratory arrest
- Unresponsive trauma
- Unresponsive babies
- Severe crush on limbs
- Extensive burns
- Near drownings
- Unresponsive with history of poisoning
- Exsanguinations hemorrhage
- Firearm wounds
Triage 1 Critical
(Red Zone) IMMEDIATE
This denotes patients who are unstable or when there is a potential loss of life or limb. For example:- Cardiac arrest
- Severe respiratory arrest
- Unresponsive trauma
- Unresponsive babies
- Severe crush on limbs
- Extensive burns
- Near drownings
- Unresponsive with history of poisoning
- Exsanguinations hemorrhage
- Firearm wounds
Triage 1 Critical
(Red Zone) IMMEDIATE
This denotes patients who are unstable or when there is a potential loss of life or limb. For example:- Cardiac arrest
- Severe respiratory arrest
- Unresponsive trauma
- Unresponsive babies
- Severe crush on limbs
- Extensive burns
- Near drownings
- Unresponsive with history of poisoning
- Exsanguinations hemorrhage
- Firearm wounds
Meet Our Specialists
View AllDr. Ahmad Sufian Bin Ab Rahman
ONCOLOGY, INTERNAL MEDICINE
Consultant Medical Oncologist and Internal Medicine Physician (Visiting)
Meet Our Specialists
View AllDr. Dharmendran Ratnasingam
GENERAL SURGERY AND UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL SURGERY
Consultant General Surgeon

