Almost all women experiences pain during the process of labor and delivery. In some societies, pain during labor is considered as natural phenomenon and should be tolerated by women. Some consider childbirth’s uterine contraction as severe and need intervention. In one study, 60% of primiparae described labor pain as severe and intolerable, and another 30% experienced moderate pain. In comparison, 45% of multiparae describe it as severe, and 30% experienced moderate pain.
There are multi-factors that influence the intensity of pain during labor such as age and parity, frequency of uterine contraction, stage of labor, fetal size and presentation, as well as psychological factors.
Women who experience pain during uterine contractions in childbirth can have adverse physiological effects such as prolong stomach highly acidic contents emptying, hyperventilation, increase blood pressure, dis-coordinate uterine contraction and reduced placental perfusion. These adverse effects can be minimized by effective pain control.
What methods of pain relief is available?
Non-pharmacological methods which might reduce use of medication to ameliorate pain
- Coping strategies and support such as prepared childbirth, support from a partner and midwives, calm breathing and massage during labor, aromatherapy, reflexology, water bath.
- Transcutaneous nerve stimulation (TENS)
- Acupuncture
Pharmacology methods which are commonly used
- Entonox- a mixture of 50% nitrous oxide and 50% oxygen, which is breath through a mask. It is quick to act, but effect only last for a short while. It does not reduce the pain completely, and cause dizziness.
- Intramuscular opiods injection which is usually injected by midwives. It takes about half an hour to work and last for a few hours. It can cause nausea and vomiting, drowsiness, and respiratory depression to the newborn.
- Epidural analgesia is the most effective way of pain relief for labor pain. This procedure is performed by the trained anesthetists under aseptic technique.
Obstetric epidural –procedures involved
First, an intravenous cannula will be inserted on the hand, in order to run intravenous drip. Then you have to sit bending forward. The anesthetist will clean the lower back with antiseptic. After identifying the point of insertion of epidural at the lower back, the anesthetist will inject local anesthetic into your skin, so that putting in the epidural needle does not usually cause much pain. An epidural catheter (a very thin tube) is then threaded through epidural needle to reach near the nerves in your spine. The epidural catheter is left in place when the needle is taken out so local anesthetic can be given via the epidural catheter to provide pain relief throughout the course of labor.
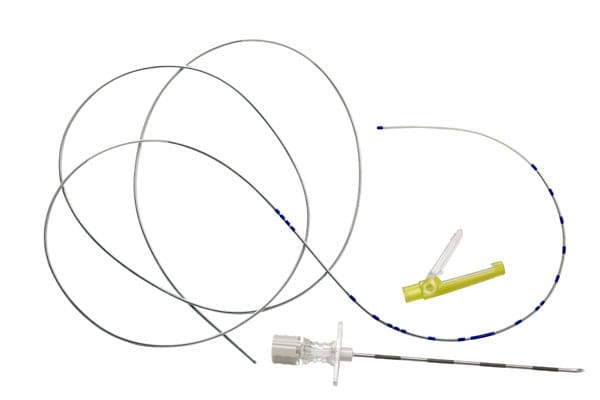
Figure 1: Image of epidural catheter and epidural needle
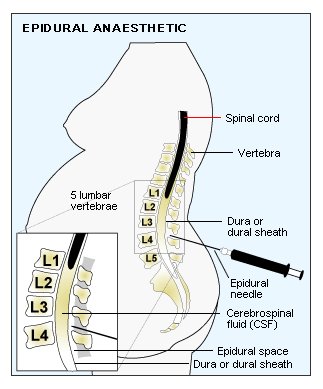
Figure 2: Site of epidural needle insertion
Benefit of epidural analgesia:
- Epidurals provide better pain relief than any other treatment.
- Generally do not affect the newborn such as respiratory depression.
- Spinal analgesia can be given first in the technique called combined spinal-epidural analgesia for a quicker effect of pain relief.
- Can be used to provide anesthesia if caesarean section is required.
Possible risks associated with epidural analgesia:
- Second stage of labor is longer.
- Higher incidence of low blood pressure and itchiness.
- May have leg weakness if higher concentration of local anesthetic is used.
- May have difficulty in passing urine temporary.
- Can develop headache which is usually self-limiting after treatment. This is caused by accidentally puncture of dural sac (bag with fluid that surround the spinal cord).
Share:
Was this article helpful?
Share:
Was this article helpful?
Health Packages
Elevate your health with tailored health packages at Columbia Asia Hospital. Take charge of your health journey today.
AIA Policyholders Self-pay Benefits
12.12 CheckJer Health Package
RM140
Find Out MorePink October 2025
From
RM80
HLA Policyholders Promo: Influenza Vaccination
RM65
Find Out MoreColumbia Asia 30th Anniversary Promotion “Maternity & Baby”
Pink October 2024
From
RM80

